Introduction
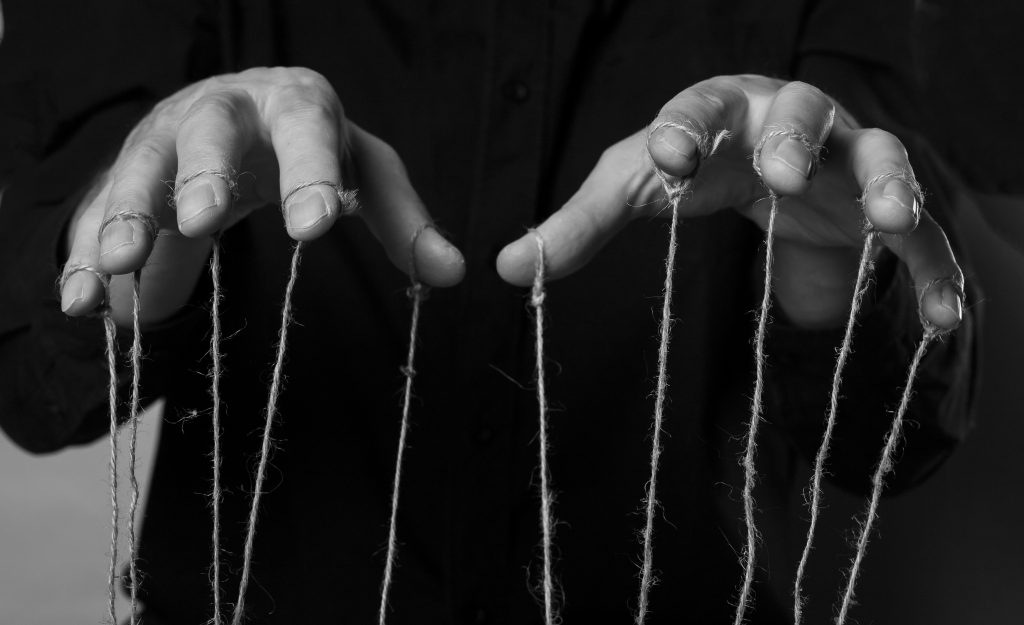
In the dynamic world of forex trading, not all market movements are driven purely by economic forces. Behind the scenes, manipulative practices can be at play, with brokers or entities pulling the strings to influence outcomes, much like a puppeteer controlling their marionettes. These hidden hands, operating with unethical motives, can steer traders toward unfavorable decisions, leading to significant financial losses. While the UAE provides a strong regulatory framework designed to protect investors, the complexity and volatility of the forex market still leave room for manipulation. This article explores how these covert practices impact the market, the legal safeguards in place, and how traders can navigate this intricate landscape to protect themselves against manipulation and hidden control.
- What is Forex Trading?
Forex trading involves the exchange of currencies on a decentralized global market, where participants aim to profit from the changes in exchange rates between different currency pairs. The forex market operates over-the-counter (OTC) and is open 24 hours a day, five days a week, allowing trades to be conducted globally across time zones. The market is split into several trading centers, including those in New York, London, Tokyo, and Sydney.
Participants in the forex market include a wide variety of actors, from individual retail traders to institutional investors such as banks, hedge funds, and multinational corporations. The market is driven by several factors, including global economic data, geopolitical events, and the monetary policies of central banks. Forex brokers provide access to this market, enabling traders to buy and sell currencies through online platforms.
Leverage is a key feature of forex trading, allowing traders to control large positions with relatively small amounts of capital. While this can magnify profits, it equally increases the risk of significant losses, particularly for inexperienced traders. As such, understanding the risks associated with leverage and the trading strategies employed is crucial for any participant in the forex market.
- How Forex Operates in the UAE
Forex trading in the UAE operates under a regulatory framework designed to protect investors and ensure the integrity of financial markets. Forex companies must either be licensed by the Securities and Commodities Authority (SCA), which oversees the mainland UAE, or the Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA), which regulates entities operating within the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC). Both bodies ensure that forex companies comply with international standards, conduct transparent operations, and adhere to strict capital requirements.
SCA Regulation
The Securities and Commodities Authority (SCA) governs forex trading within the UAE mainland under the provisions of Federal Law No. (4) of 2000 Regarding the Emirates Securities and Commodities Authority and Market. The SCA’s regulatory framework is designed to ensure that licensed brokers operate with transparency and accountability. Article 4 of this law gives the SCA the power to issue licenses, while Article 26 mandates that brokers maintain sufficient capital reserves and provide regular financial reporting to the regulatory body. This ensures that forex brokers operating in the UAE mainland have the financial stability required to protect clients’ funds and avoid insolvency risks.
DFSA Regulation
Within the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC), forex brokers are regulated by the Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA). The DFSA implements international best practices and standards to ensure that brokers maintain market integrity and provide a secure environment for forex trading. Companies operating under DFSA supervision must adhere to strict reporting obligations and anti-fraud measures, ensuring that traders are protected from unscrupulous practices.
In addition to these regulatory bodies, forex brokers in the UAE must comply with Federal Law No. (20) of 2018 on Anti-Money Laundering (AML), which requires brokers to conduct thorough customer due diligence (CDD), report suspicious transactions, and maintain strict records to prevent illicit activities such as money laundering or the financing of terrorism. Brokers must verify the identities of their clients and continually monitor transactions to ensure compliance with both local and international financial regulations.
- Common Fraudulent Practices in Forex Trading
Despite the stringent regulations in place within the UAE, fraudulent activities remain a significant concern in the forex industry. Like similar cases that have been handled by Clout in the region, unethical brokers employ a variety of schemes and tactics to deceive traders, particularly those who are inexperienced, leading to substantial financial losses. Below are some of the most common fraudulent practices observed in the forex market.
Unlicensed Brokers
One of the most prevalent risks faced by traders is engaging with unlicensed forex brokers. These brokers operate outside the regulatory frameworks of the Securities and Commodities Authority (SCA) or the Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA), making them largely unaccountable to any oversight body. Unlicensed brokers often lure traders by promising high returns, offering overly generous leverage, or marketing themselves as low-cost alternatives to regulated brokers. However, since these brokers do not comply with local regulatory standards, traders face significant risks, including the possibility of the broker disappearing with their funds or manipulating trades to their detriment.
Investors may find it difficult to recover their funds once a problem arises with an unlicensed broker. Without proper licensing, there is no legal recourse through the regulatory bodies, leaving traders vulnerable. It is, therefore, crucial for traders to verify the licensing status of any forex broker before engaging in trading activities.
Manipulated Trading Platforms
Another common practice among fraudulent brokers involves the manipulation of trading platforms. Some brokers use software that deliberately skews prices, causing artificial price spikes or delays in trade execution. These price discrepancies benefit the broker at the expense of the trader, who may find themselves entering or exiting trades at less favorable rates than what would occur in a legitimate, transparent market.
For example, a manipulated platform might delay the execution of a trade until the market price has moved against the trader, allowing the broker to profit from the unfavorable position. Such manipulations are difficult to detect for most retail traders, especially those who lack extensive experience or technical expertise. This type of fraud can result in substantial financial losses, with traders often unaware that the platform itself is the source of their problem.
Ponzi Schemes
Ponzi schemes are another form of fraud prevalent in the forex industry. In such schemes, a broker promises guaranteed returns to investors, often claiming that they can double or triple investments in a short period. However, rather than generating legitimate profits through forex trading, the broker uses the funds of new investors to pay returns to earlier participants, creating the illusion of profitability. Eventually, the scheme collapses when the broker can no longer attract new investors, leaving most participants with significant financial losses.
These schemes are particularly dangerous because they prey on individuals’ trust and often have an appearance of legitimacy. Brokers running Ponzi schemes may initially pay out small returns to encourage additional investments, further trapping victims in the scam. It is important for traders to be wary of brokers who promise unrealistically high returns with minimal risk.
Excessive Leverage
Leverage is a double-edged sword in forex trading. While it can amplify profits, it equally increases the risk of substantial losses. Some brokers offer excessive leverage ratios, such as 1:500, enticing traders with the prospect of controlling large positions with minimal capital. However, such high leverage is highly risky, especially for inexperienced traders, as it can lead to the rapid depletion of capital in a volatile market.
Unscrupulous brokers may encourage clients to use high leverage without clearly explaining the associated risks, knowing that the increased volatility will often lead to the trader losing their position. These brokers profit from their clients’ losses, as their business model may be designed to capitalize on trading volume rather than client success.
Withdrawal Issues
One of the most frustrating issues traders face with fraudulent brokers is difficulty in withdrawing their funds. Some brokers impose arbitrary restrictions or high fees on withdrawals, effectively trapping clients’ capital in their trading accounts. In more severe cases, the broker may refuse withdrawal requests altogether, citing fabricated violations of the terms and conditions or claiming that additional documentation is required.
These withdrawal restrictions are often not clearly disclosed upfront, and traders only discover them when they attempt to access their funds. This practice is highly deceptive and represents one of the most egregious forms of fraud in the forex industry, as it directly impacts the trader’s ability to control their own money.
- Hedging in Forex Trading
Hedging is a risk management strategy that forex traders use to protect their positions against unfavorable market movements. In essence, hedging involves taking an offsetting position in a related asset to minimize potential losses. For example, if a trader is long on a currency pair and anticipates a potential decline in value, they may take a short position in a correlated currency or asset to offset any losses in their primary position. This strategy can help mitigate risk and provide more stability in volatile markets.
Hedging Tools and Their Importance in the UAE
Forex brokers in the UAE, regulated by the Securities and Commodities Authority (SCA) and the Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA), offer various hedging tools to their clients. These tools are designed to give traders greater control over their risk exposure and enable them to navigate periods of market uncertainty more effectively. For instance, some brokers offer options and futures contracts, which can be used to hedge against adverse currency movements.
The availability of hedging tools is particularly important in a market as volatile as forex, where prices can swing significantly in a short period due to factors such as geopolitical events, economic data releases, and central bank interventions. By employing hedging strategies, traders can lock in profits or protect themselves from major losses, making it a critical tool for both retail and institutional investors.
Limitations and Restrictions on Hedging
While hedging can be highly beneficial, not all brokers provide optimal hedging facilities. Some impose limitations on the size of hedged positions or restrict the types of assets that can be used for hedging purposes. Additionally, certain brokers may charge higher fees for using hedging strategies, making it more expensive for traders to protect their investments.
Traders should also be aware that some brokers discourage hedging by offering unfavorable terms or by requiring additional margin to maintain hedged positions. These restrictions can undermine the effectiveness of a trader’s risk management strategy and leave them exposed to greater risk than anticipated.
Regulatory Oversight on Hedging
Regulated brokers under the SCA and DFSA are required to disclose the risks and fees associated with hedging to ensure that clients fully understand the terms under which these strategies can be used. This transparency is crucial in helping traders make informed decisions and protecting them from unfair practices. Both regulatory bodies also monitor brokers to ensure that they do not engage in practices that undermine the integrity of hedging tools or mislead clients about the potential risks involved.
By leveraging hedging strategies effectively, traders can better manage their risk exposure in a dynamic and often unpredictable forex market, giving them greater control over their trading outcomes.
- Money Laundering and Forex Trading: A Dangerous Nexus
The forex market, due to its liquidity and decentralized nature, is often targeted by criminals for money laundering purposes. Money laundering involves disguising the origins of illegally obtained funds, making them appear legitimate. The sheer volume of transactions and the global nature of forex trading provide a convenient avenue for criminals to launder money by moving funds across borders, often through multiple financial institutions and trading platforms.
How Forex Can Be Exploited for Money Laundering:
- Layering through Forex Transactions: Criminals may use forex transactions to move funds across different jurisdictions, converting illicit funds into various currencies and then back again, thereby obscuring the trail of the money. This process, known as layering, makes it more difficult for authorities to trace the original source of the funds.
- Use of Shell Companies: Shell companies, often registered in offshore jurisdictions with lax regulatory oversight, can be used to facilitate money laundering through forex trading. These companies appear to engage in legitimate trading activities, but in reality, they are conduits for moving illicit funds. Forex brokers dealing with such companies may unknowingly—or, in some cases, knowingly—become part of a larger money-laundering operation.
- Converting to Cryptocurrency: With the rise of cryptocurrency trading, some forex brokers have begun offering the option to convert fiat currencies into cryptocurrencies. Cryptocurrencies provide an additional layer of anonymity, making it harder for law enforcement agencies to trace the flow of illicit funds. Criminals can take advantage of this to further conceal the origins of their money.
To combat such activities, the UAE enforces strict anti-money laundering laws under Federal Law No. (20) of 2018 on Anti-Money Laundering and Combating the Financing of Terrorism. Forex brokers are required to conduct thorough due diligence on their clients, report suspicious activities to the Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU), and maintain detailed records of all transactions. Failure to comply with these requirements can result in severe penalties, including fines and license revocation.
- How to File a Complaint Against a Forex Company and Legal Recourse
When an investor faces fraud or unethical practices from a forex broker in the UAE, there are several steps that can be taken to seek legal recourse. These steps typically involve engaging with regulatory authorities, escalating the matter to law enforcement, and potentially pursuing civil or criminal action in court.
- Filing a Complaint with Regulatory Authorities
It is preferable to file a formal complaint through a lawyer with the relevant regulatory authority, either the Securities and Commodities Authority (SCA) or the Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA), depending on where the broker is licensed. A lawyer can ensure that the complaint is filed correctly, with all relevant documentation, such as transaction records, trading history, and communications between the investor and the broker.
SCA Complaint Process:
- Complaints can be filed directly with the SCA if the broker is licensed under their authority. The SCA will investigate the matter and, if the broker is found to have violated regulatory standards, may impose penalties such as fines, suspension, or revocation of the broker’s license.
DFSA Complaint Process:
- If the broker is licensed by the DFSA in the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC), the complaint should be filed with the DFSA. Similar to the SCA, the DFSA will investigate the broker’s conduct and take appropriate action if regulatory violations are identified.
- Escalation to the Police and Public Prosecutor
If the regulatory complaint does not resolve the issue or if there are indications of criminal activity, such as fraud or embezzlement, the next step is to escalate the matter to the police. Filing a report at the local police station initiates a criminal investigation, during which law enforcement agencies will collect evidence and interview the parties involved.
If the police determine that a crime has been committed, the case will be referred to the Public Prosecutor, who will review the evidence and, if warranted, file criminal charges against the forex broker. The Public Prosecutor can also freeze the broker’s assets during the investigation to prevent further harm to investors.
Once the case reaches the UAE courts, legal proceedings will commence. If the broker is found guilty, they may face criminal penalties, including fines and imprisonment, and the court may order compensation for the affected investors.
- Responsibility of Managers and Directors
Under UAE law, the managers and directors of a forex company can be held personally liable for any misconduct or fraudulent activities that occur under their leadership. These individuals have a fiduciary duty to act in the best interests of the company’s clients and shareholders. If they are found to have knowingly engaged in illegal practices or allowed such practices to continue unchecked, they may face both criminal and civil penalties, including imprisonment and fines. In some cases, the courts may also order the seizure of personal assets to compensate victims of fraud.
- The Role of Offshore Companies in Hiding Ownership
A significant challenge in the legal pursuit of fraudulent forex brokers is the use of offshore companies to hide ownership. Many brokers operate through parent companies or holding companies registered in jurisdictions such as the Seychelles or the British Virgin Islands (BVI). These jurisdictions often have lax regulatory requirements and do not mandate the disclosure of ultimate beneficial owners (UBOs), allowing the true owners to remain anonymous and shielded from legal action.
How Offshore Structures Work:
- Offshore companies are used to obscure the identities of those who control forex operations. The parent company is typically registered in a jurisdiction with low transparency requirements, allowing the broker to operate without revealing the true ownership structure.
- If a forex company is found guilty of fraud, pursuing legal action against the offshore parent company can be difficult, as these jurisdictions often do not cooperate with international investigations.
Implications for Legal Action:
- The UAE’s Anti-Money Laundering (AML) laws empower regulatory bodies to investigate offshore companies and trace their ownership structures. However, the process can be slow and complicated, requiring cooperation from multiple jurisdictions. In such cases, it is critical to engage legal experts who specialize in international corporate law and financial fraud to navigate the complexities of pursuing claims across borders.
Conclusion
Forex trading in the UAE is heavily regulated to protect investors and maintain market integrity. However, the forex industry remains vulnerable to fraudulent practices, especially when dealing with unlicensed brokers or companies that obscure ownership through offshore entities. Investors who fall victim to such schemes have several avenues for legal recourse, starting with complaints to the Securities and Commodities Authority (SCA) or the Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA) and escalating to the police and courts if necessary.
With Clout Law Firm and its team of highly experienced legal professionals, investors can effectively navigate the complex regulatory landscape and pursue justice against fraudulent brokers. Clout’s extensive experience in handling multi-million-dollar complaints and representing forex companies, both in regulatory matters and in defending clients abroad, positions the firm as a leading authority in the field. The UAE’s legal and regulatory framework offers a strong mechanism for investor protection, but with Clout’s expertise, clients are better equipped to avoid the pitfalls set by unscrupulous operators in the forex market, ensuring that their interests are safeguarded at every step.
Disclaimer: This article was prepared by Clout Law Firm. The content may have been structured and proofread using reputable AI tools to ensure accuracy and clarity. However, the information provided is for general informational purposes only and should not be construed as legal advice. For specific legal guidance, please contact Clout Law Firm at info@clout.ae.